
Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. You might think that if there is only one slit, there wouldnt be any wave. We recommend using aĪuthors: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs Both light waves and radio waves are examples of electromagnetic waves. Use the information below to generate a citation. The screen is now moved 10cm closer to the slit and the width of the maxima decreases to 9cm. Figure 5.6 (a) Grating intensity pattern and single slit diffraction pattern. The diffraction pattern is projected onto a screen where the width of the principal maximum is 10cm. return to the vector nature of the electric field in the light wave. Then you must include on every digital page view the following attribution: Laser light of wavelength 600nm passes through a narrow slit. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format, Then you must include on every physical page the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the previous page: next page: Reflection 2-Slit Diffraction. Note that the central maximum is larger than those on either side, and that the intensity decreases rapidly on either side. 2 Electric Field Electric Charge Electrical Conductor / Insulator. Figure 27.21 shows a single slit diffraction pattern. However, when rays travel at an angle θ θ size 12, and we see that a destructive minimum is obtained when this distance is an integral multiple of the wavelength. Light passing through a single slit forms a diffraction pattern somewhat different from those formed by double slits or diffraction gratings. 9.1 the electromagnetic field of a plane wave, of. When they travel straight ahead, as in Figure 27.22(a), they remain in phase, and a central maximum is obtained. diffraction and interference patterns for single and double slits measured. (Each ray is perpendicular to the wavefront of a wavelet.) Assuming the screen is very far away compared with the size of the slit, rays heading toward a common destination are nearly parallel. These are like rays that start out in phase and head in all directions.


According to Huygens’s principle, every part of the wavefront in the slit emits wavelets. Light passing through a single slit is diffracted in all directions and may interfere constructively or destructively, depending on the angle.
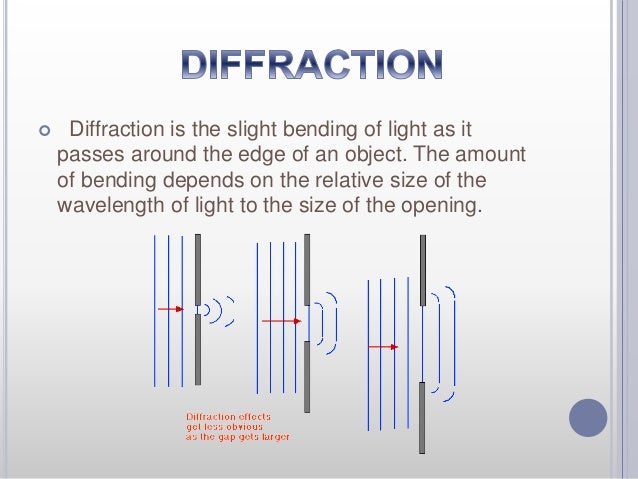
Here we consider light coming from different parts of the same slit. The analysis of single slit diffraction is illustrated in Figure 27.22. (b) The drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. The first minimum is at, sin 2 2 a Hence angular width of diffraction peak is: a (1.6) 1.5 Diffraction from a finite slit: phasor treatment Figure 1.7 Construction showing elements at extreme edges of aperture contributing first and last phasors-10 -5 0 5 10 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1. Figure 27.21 (a) Single slit diffraction pattern. Figure 1.6 Intensity pattern from single slit, I p I(0)sinc2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
